
ACLS PALS BLS Exam Prep iOS and Android App
Empower your healthcare certification journey with the ultimate 'ACLS PALS BLS Exam Prep' app!
Designed to provide a rigorous and adaptive learning environment, our app is the cornerstone of effective preparation for the Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support (ACLS), Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS), and Basic Life Support (BLS) exams.
Engage with a broad spectrum of practice questions, meticulously formulated to cover every critical topic within these essential medical certifications.
Every question comes with an in-depth explanation, offering valuable insights to enhance your understanding and ensure you are exam-ready.
Key Features:
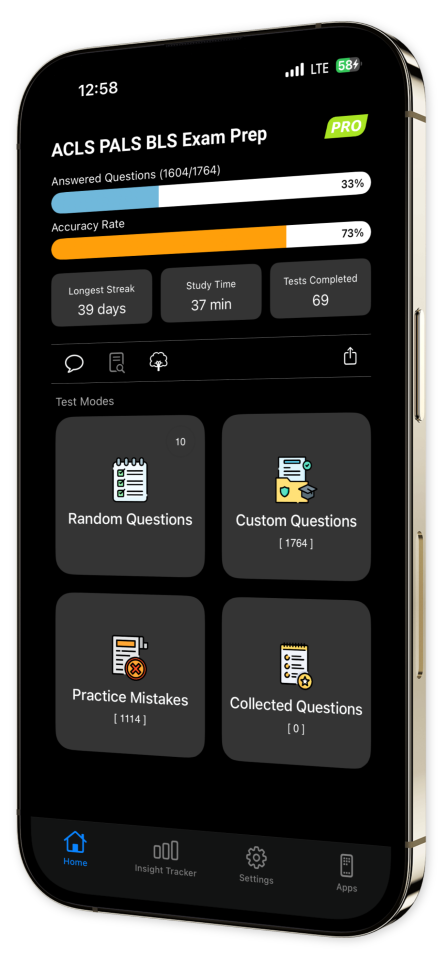
Extensive Question Bank: Navigate through an expansive library of questions designed to ensure a robust and comprehensive understanding of ACLS, PALS, and BLS protocols.
In-Depth Explanations: Delve into rich, detailed rationales with every question, fostering deeper learning and better retention.
Customizable Quizzes: Tailor your study experience by creating personalized quizzes targeted on specific topics or question types, focusing your preparation where it's needed most.
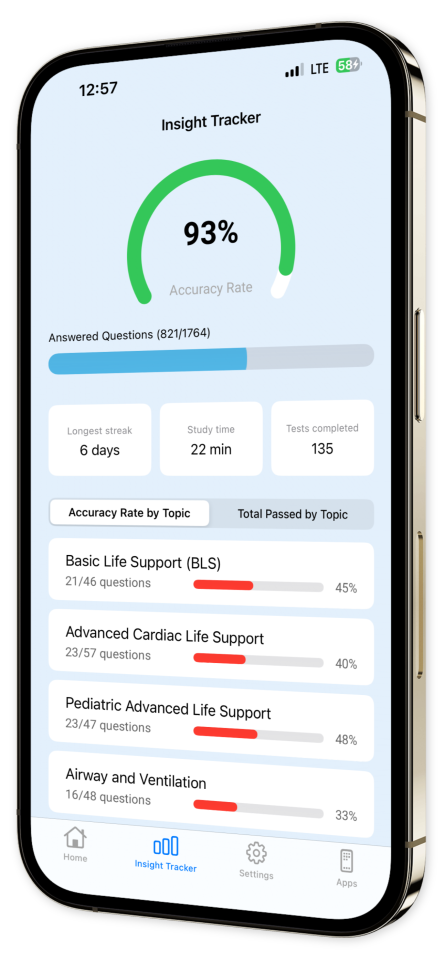
Progress Tracking: Monitor your improvement with our intuitive tracking features and stay consistently informed about your learning journey.
Offline Access: Break free from internet constraints! Study anytime, anywhere, even offline, perfect for those constantly on the move.
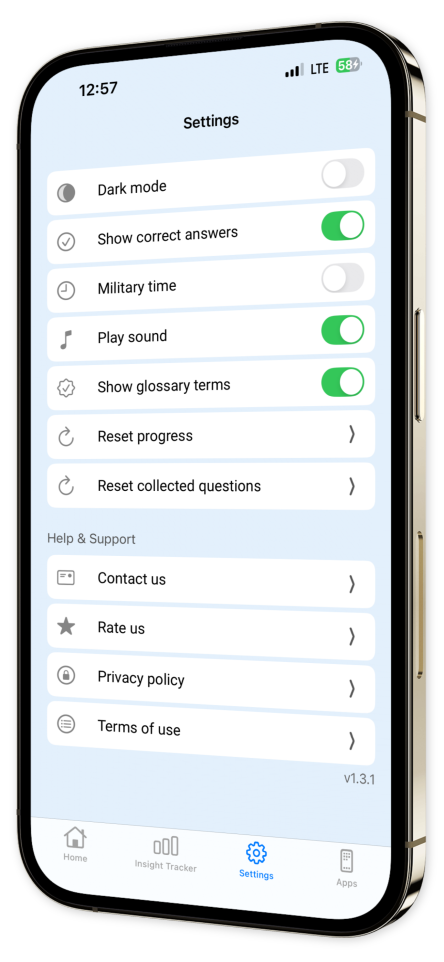
User-Friendly Interface: Seamlessly navigate through our app with an intuitive design that prioritizes your learning experience.
Download 'ACLS PALS BLS Exam Prep' today and embark on a path to comprehensive certification success with an app that brings efficiency and ease to exam preparation!
Stay ahead in your career.
Elevate your learning.
Become certified with confidence.
Content Overview
Explore a variety of topics covered in the app.
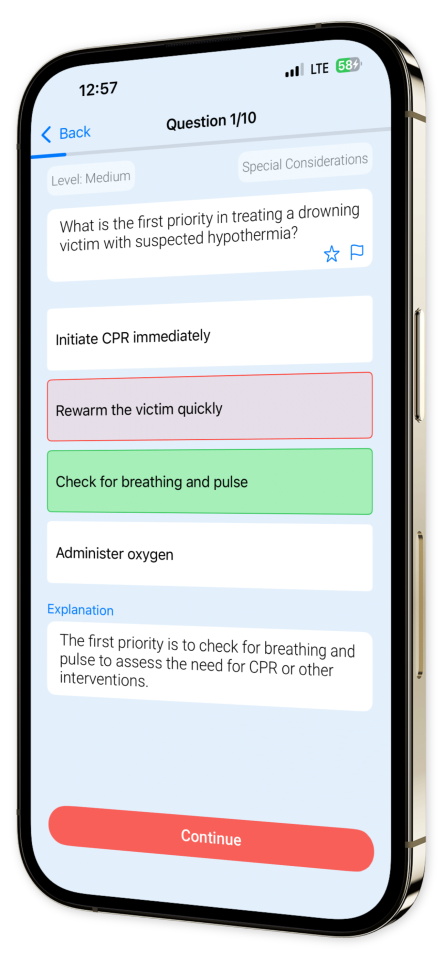
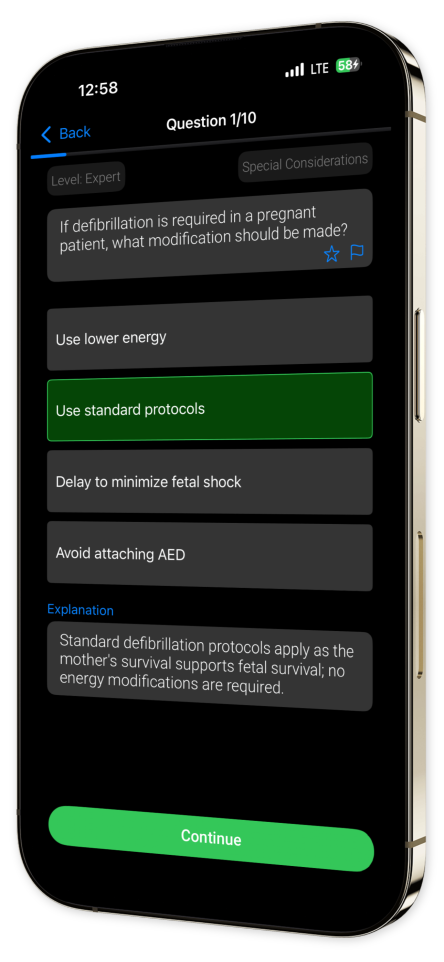
Example questions
Let's look at some sample questions
What compression-to-ventilation ratio should be used with 2 rescuers on a child?
30:215:25:120:2
With 2 rescuers on a child, the correct ratio is 15:2. This helps provide sufficient ventilation.
In infant CPR with 2 rescuers, what is the proper compression-to-ventilation ratio?
30:215:210:120:2
For 2 rescuers in infant CPR, the correct ratio is 15:2, allowing rapid compressions with adequate breaths.
What compression-to-ventilation ratio is used in single rescuer child CPR?
15:230:220:25:1
The single rescuer child CPR ratio is the same as for adults, 30:2, to ensure enough compressions.
A rescuer is alone performing CPR on a newborn. What is the correct compression-to-ventilation ratio?
15:230:23:15:1
For newborns, especially without advanced airway, the correct ratio is 3:1 according to neonatal resuscitation guidelines.
When performing CPR, one rescuer on an adult should provide compressions and breaths at which ratio?
15:230:220:1010:1
The standard ratio for adult CPR by one rescuer is 30:2, ensuring effective compressions and ventilation.
In adult CPR, what is the recommended compression-to-ventilation ratio during one-rescuer CPR without an advanced airway?
30:215:210:120:2
The American Heart Association recommends a compression-to-ventilation ratio of 30:2 for adult CPR during one-rescuer situations without an advanced airway.
For a child in two-rescuer CPR, what is the compression-to-ventilation ratio?
30:215:220:210:1
The recommended compression-to-ventilation ratio for two-rescuer CPR in children is 15:2, according to the American Heart Association.
How many chest compressions should be delivered before giving 2 breaths in a single-rescuer adult CPR?
15302520
In adult CPR, a solitary rescuer should give 30 chest compressions followed by 2 rescue breaths as per AHA guidelines.
Which compression-to-ventilation ratio is used for infants during two-rescuer CPR?
30:215:210:120:2
In two-rescuer infant CPR, AHA recommends a 15:2 compression-to-ventilation ratio.
In a multi-rescuer situation, what is the compression-to-ventilation ratio for newborns if not intubated?
3:115:230:210:1
For CPR on newborns not intubated, the compression-to-ventilation ratio is 3:1 as per the American Heart Association.